Introduction
Menstruation, commonly known as a period, is a natural and essential part of the reproductive cycle. Every month, the female body prepares for a potential pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterus sheds its lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding. This process is a sign of health and fertility, and it’s a journey that most women embark on from puberty until menopause.
What is Menstruation?
Menstruation is the monthly release of blood and tissue from the uterus through the vagina. Hormones control this process, and it happens in cycles. The first day of bleeding marks the beginning of a new menstrual cycle, which typically lasts between 21 and 38 days. However, the length can vary among individuals and at different life stages.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
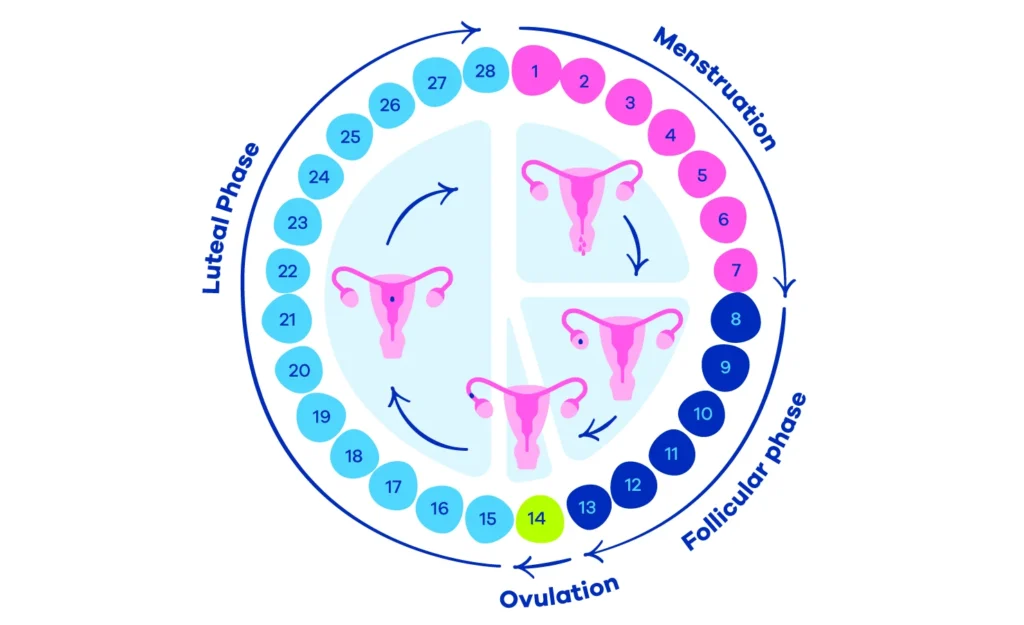
The menstrual cycle consists of four main phases: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
- Menstruation: This phase begins when an egg from the previous cycle isn’t fertilised. The thickened lining of the uterus, prepared for a potential pregnancy, sheds and exits the body through the vagina. This shedding is the menstrual flow, often referred to as a period.
- The Follicular Phase: This phase starts on the first day of menstruation and ends with ovulation. The body begins to prepare another egg for ovulation.
- Ovulation: This is the release of a mature egg from the ovary. It usually happens about two weeks before the start of the next period.
- The Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy. If the egg isn’t fertilised, the cycle repeats.
Common Symptoms and Menstrual Problems
During menstruation, women may experience various symptoms such as abdominal or pelvic cramping, lower back pain, bloating, sore breasts, food cravings, mood swings, and fatigue. These symptoms are often part of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which can start a few days before the period.
Some women may face menstrual problems like heavy or painful periods, irregular periods, or the absence of periods. These could be signs of health issues like hormonal imbalances, eating disorders, or certain reproductive conditions. If you notice significant changes in your menstrual cycle or if your symptoms interfere with your daily life, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While menstruation is a natural process, it’s crucial to monitor your menstrual health and seek medical advice if you notice any unusual changes. These could include periods that last more than a week, extremely heavy bleeding, severe pain, periods that stop suddenly for more than 90 days (and you’re not pregnant), or periods that become irregular after having been regular.
Understanding menstruation and its impact on your body is an essential part of women’s health. It’s more than just a monthly occurrence; it’s a barometer of your overall health and well-being.