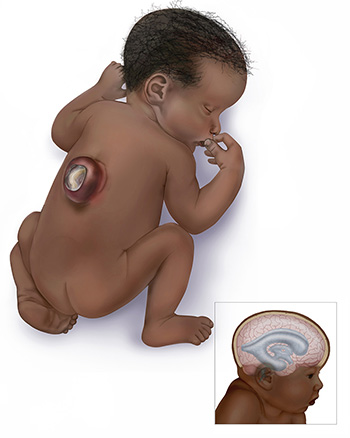
You may have heard the term “congenital abnormalities” or “birth defects” and be wondering what they are and what causes them. In this article, we will explain these conditions in simple language to help you understand them better.
Definition
Congenital abnormalities are deformities that occur during the development of the baby and can affect various parts of the body. They are also known as birth defects or congenital malformations. These conditions can range from mild to severe and can be identified before or after birth.
Causes/Risk factors
The causes of congenital abnormalities are not fully understood, but they can result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of these factors include:
- Inherited genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities
- Exposure to harmful substances, such as alcohol, drugs, or chemicals
- Maternal infections during pregnancy
- Maternal chronic diseases, such as diabetes
Types
There are several types of congenital abnormalities, and they can affect any part of the body. Here are some of the most common types:
- Structural abnormalities: These are physical defects that affect the structure of the body, such as cleft lip and palate, heart defects, and neural tube defects.
- Functional abnormalities: These are defects that affect how the body functions, such as hearing or vision loss.
- Metabolic abnormalities: These are abnormalities that affect the body’s metabolism, such as phenylketonuria (PKU).
- Chromosomal abnormalities: These are abnormalities that occur when there is a problem with the chromosomes, such as Down syndrome.
Clinical Manifestations
The clinical manifestations of congenital abnormalities can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some abnormalities may be visible at birth, while others may not be apparent until later in life. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Abnormalities in body structure or shape
- Delayed development or growth
- Intellectual disability
- Difficulty with movement or coordination
- Breathing problems
- Heart problems
- Digestive problems
- Hearing or vision problems
Treatment options
The treatment options for congenital abnormalities depend on the type and severity of the abnormality. Some treatment options include:
- Surgery: Some physical deformities, such as cleft lip or clubfoot, can be corrected with surgery.
- Medication: Some metabolic abnormalities, such as PKU, can be treated with medication.
- Therapies: Some functional abnormalities, such as hearing loss, can be treated with therapies such as hearing aids or cochlear implants.
- Supportive care: Many congenital abnormalities require ongoing supportive care, such as physical therapy or occupational therapy.
Education on Prevention
While not all congenital abnormalities can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of having a baby with a birth defect. Some things you can do include:
- Getting early and regular prenatal care
- Avoiding alcohol, drugs, cigarettes, or any tobacco-containing substance during pregnancy
- Managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, before and during pregnancy
- Taking folic acid supplements before and during pregnancy
- Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and radiation.
By adopting these preventative measures, the rate of congenital abnormalities can be significantly reduced, resulting in healthier pregnancies and healthier babies.