Menstrual period health is a critical aspect of every woman’s reproductive journey. It is a natural and vital part of the female reproductive cycle. Each month, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterus sheds its lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding. This cycle begins from puberty and continues until menopause and is often seen as a barometer of overall health.
What is Menstruation?
Menstruation is the monthly release of blood and tissue from the uterus through the vagina. Hormones control this process, and it happens in cycles. The first day of bleeding marks the beginning of a new menstrual cycle, which typically lasts between 21 and 38 days. However, the length can vary among individuals and at different life stages.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
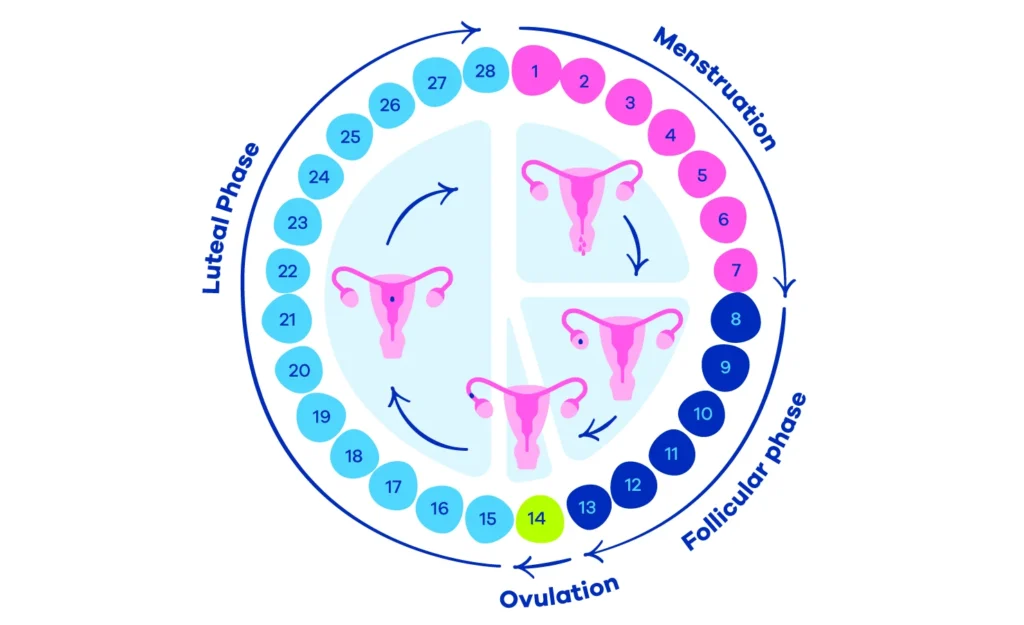
The menstrual cycle consists of four main phases: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
- Menstruation: The menstrual period begins when the egg released in the previous cycle is not fertilized. The uterus sheds its lining, exiting the body through the vagina. This process often includes blood clots when on period, which may be normal or a sign of underlying issues.
- The Follicular Phase: This phase starts on the first day of menstruation and ends with ovulation. The body begins to prepare another egg for ovulation.
- Ovulation: This is the release of a mature egg from the ovary. It usually happens about two weeks before the start of the next period.
- The Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy. If the egg isn’t fertilised, the cycle repeats.
Common Symptoms and Menstrual Problems
Many experience symptoms like cramps, fatigue, bloating, or mood changes during their menstrual period. These symptoms, often called PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome), can start before bleeding begins.
However, some women face more severe challenges, including abnormal periods, heavy flow, or menstrual period with blood clots. Large or frequent clots and period issues may be caused by blood clotting menstruation disorders or hormonal imbalances. Explore more on symptoms at YourPeriod.ca.
Menstruation clots can signal conditions like fibroids, thyroid issues, or reproductive system disorders. Inconsistent or missed periods could also indicate irregular cycles that need medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While menstruation is a natural process, it’s crucial to monitor your menstrual health and seek medical advice if you notice any unusual changes. These could include periods that last more than a week, extremely heavy bleeding, severe pain, periods that stop suddenly for more than 90 days (and you’re not pregnant), or periods that become irregular after having been regular.
Understanding menstruation and its impact on your body is an essential part of women’s health. It’s more than just a monthly occurrence; it’s a barometer of your overall health and well-being.
In such cases, consult a healthcare professional. You can also refer to this CDC menstrual hygiene guide.Doctors may recommend a contraceptive to regulate periods, especially for those experiencing cycle irregularities or hormone-related concerns.
Your menstrual period is more than a monthly occurrenceit’s a key indicator of your health. Being aware of changes in your cycle, symptoms like menstruation clots, and knowing when to seek help is essential. Understanding your body empowers you to take control of your health and well-being.